Java 14 – Record data class
This article is introducing the Java 14 new feature – record or data class, defined in JEP 359.
P.S This record data class is a preview feature
Why record?
Java is too verbose, if we want to declare a class, we need to create a lot of tedious and repetitive methods like constructors, accessors, equals(), hashCode(), toString(). Finally, Java 14 introduced the record class to simplify the process by automatically creating all the tedious methods.
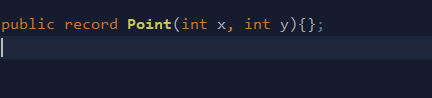
A record data class.
public record Point(int x, int y){};
1. Decompile the Java 14 record class.
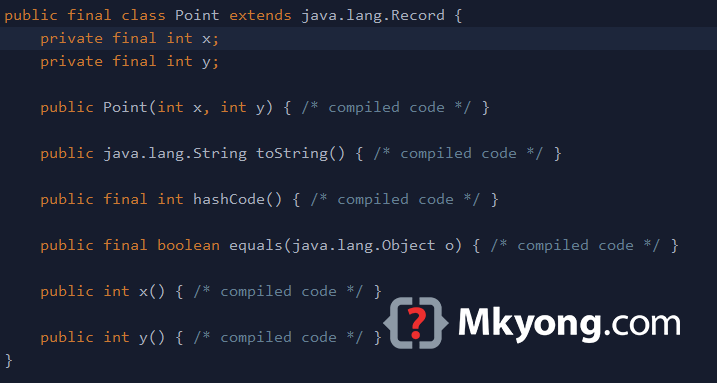
Try to decompile the above Point.class, and we will get the following source code.
// IntelliJ API Decompiler stub source generated from a class file
// Implementation of methods is not available
package com.mkyong.java14.jep359;
public final class Point extends java.lang.Record {
private final int x;
private final int y;
public Point(int x, int y) { /* compiled code */ }
public java.lang.String toString() { /* compiled code */ }
public final int hashCode() { /* compiled code */ }
public final boolean equals(java.lang.Object o) { /* compiled code */ }
public int x() { /* compiled code */ }
public int y() { /* compiled code */ }
}
Java 14 record will generate the following variables and methods automatically.
- final class extends
java.lang.Record. - private final instance variables.
- constructors, (with instance variables as arguments)
toString()hashCode()andequals(), for object comparation.getter()for the instance variable, no setters, all final variables.
That’s good, and it saved us a few clicks in IDEs.
2. How to use Java 14 Record?
This example shows you how to use a record class.
public record Point(int x, int y){};
package com.mkyong.java14.jep359;
public class PointApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// constructor Point(int x, int y)
Point p1 = new Point(10, 20);
// getters int x()
System.out.println(p1.x()); // 10
// getters int y()
System.out.println(p1.y()); // 20
Point p2 = new Point(11, 22);
System.out.println(p2.x()); // 11
System.out.println(p2.y()); // 22
Point p3 = new Point(10, 20);
System.out.println(p3.x()); // 10
System.out.println(p3.y()); // 20
// hashCode and equals
System.out.println(p1.hashCode()); // 330
System.out.println(p2.hashCode()); // 363
System.out.println(p3.hashCode()); // 330
System.out.println(p1.equals(p2)); // false
System.out.println(p1.equals(p3)); // true
System.out.println(p1.equals(p1)); // true
// toString()
System.out.println(p1); // Point[x=10, y=20]
System.out.println(p2); // Point[x=11, y=22]
System.out.println(p3); // Point[x=10, y=20]
}
}
Output
10
20
11
22
10
20
330
363
330
false
true
true
Point[x=10, y=20]
Point[x=11, y=22]
Point[x=10, y=20]
Java developer’s life is much simple now 🙂
3. Override the default methods of Record.
3.1 Review a Location record class, we will override the default record’s constructor and toString().
package com.mkyong.java14.jep359;
public record Location(double latitude, double longitude) {
// override record default constructor
public Location {
this.latitude = latitude * 3;
this.longitude = longitude * 3;
}
// override record toString
@Override
public String toString() {
return "GPS Location{" +
"latitude=" + latitude +
", longitude=" + longitude +
'}';
}
}
3.2 Test it.
package com.mkyong.java14.jep359;
public class LocationApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Location loc = new Location(10, 20);
System.out.println(loc);
}
}
Output
GPS Location{latitude=30.0, longitude=60.0}
4. Is Record Serializable?
Can we read or write the record class to a file? The answer is yes, makes record class implements Serializable and it works.
package com.mkyong.java14.jep359;
import java.io.*;
record GPS(double latitude, double longitude) implements Serializable {
};
public class Java14FileApp {
private static final String FILE_PATH = "location.obj";
public static void main(String[] args) {
GPS obj = new GPS(10, 20);
save(obj, FILE_PATH);
GPS result = read(FILE_PATH);
System.out.println(result);
}
private static void save(GPS obj, String path) {
try (ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(path))) {
oos.writeObject(obj);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static GPS read(String path) {
GPS result = null;
try (ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(path))) {
result = (GPS) ois.readObject();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
}
Output
GPS[latitude=10.0, longitude=20.0]
5. Preview Language Feature
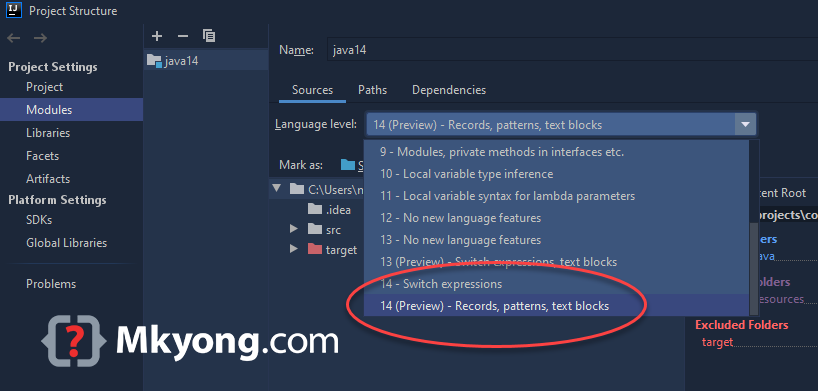
5.1 This record class is a preview feature. We need to use the --enable-preview option to enable it manually.
$ javac --enable-preview --release 14 Point.java
$ java --enable-preview Point
5.2 For IntelliJ IDE, please update to the latest version 2020.1.1; it should support the Java 14 new preview features.
Download Source Code
$ git clone https://github.com/mkyong/core-java
$ cd java-14
It looks like https://projectlombok.org/
Is Record class replacing java.lang.Object?
Thank for this article